Knee Replacement Surgery Singapore
Information reviewed by: Dr Foo Gen Lin | Last updated: Feb 20, 2026
Is severe knee arthritis affecting your ability to walk or enjoy daily life? Dr Foo provides comprehensive evaluation and personalised surgical care to help relieve pain and restore mobility.
MBBS (University of London) | MMed (Ortho) | FRCSEd (Ortho) | FAMS (Ortho)


What Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
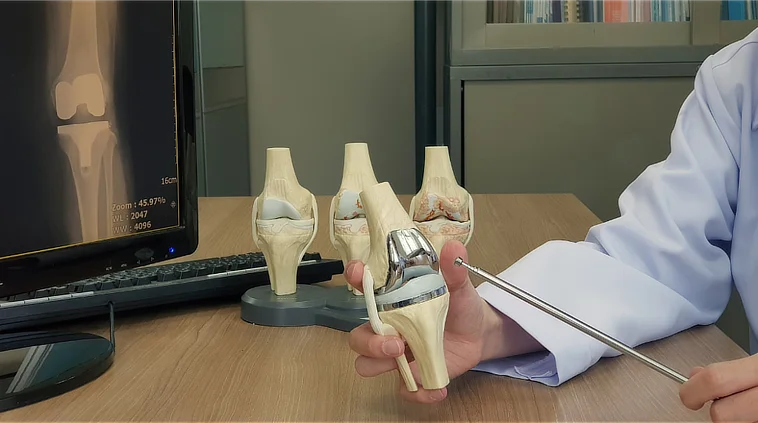
Knee replacement surgery is a medical procedure that involves replacing damaged
joint surfaces with artificial implants to relieve pain and restore mobility in
individuals with severe knee damage.
Whether caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or injury, the procedure
can significantly improve knee function and overall quality of life.
Why Is Knee Replacement Surgery Required?
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended when non-surgical treatments, such as
physiotherapy, medication, joint injections, or lifestyle modifications, are no longer effective,
and persistent pain and stiffness interfere with daily activities.
The most common reasons for knee replacement include:
- Osteoarthritis – A degenerative joint condition where cartilage wears down over time and long-term use, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, especially in older adults.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – An autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of the joint lining, resulting in cartilage destruction and joint deformity.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis – Joint damage that develops after a knee injury, such as fractures or ligament tears. This may lead to long-term pain and stiffness.
Partial vs. Total Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery can be classified into partial knee replacement and total knee replacement, depending on the severity and location of joint damage.
| Feature | Partial Knee Replacement | Total Knee Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Extent of Surgery | Only one compartment is replaced | Entire knee joint is replaced |
| Recovery Time | Faster | Longer |
| Recommended For | Localised knee damage | Severe arthritis or joint damage |
| Durability | 70% last 25 years | 82% last 25 years |
| Preservation of Healthy Tissue | Yes | No |
What Is a Total Knee Replacement?
Total knee replacement (total knee arthroplasty) involves replacing the entire knee
joint. The procedure removes damaged cartilage and bone from the femur (thigh bone),
tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap), replacing them with prosthetic components.
This option is generally suitable for individuals with extensive knee joint damage affecting multiple compartments of the knee.
What Is a Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement (unicompartmental knee arthroplasty) is performed when only one
section of the knee joint is damaged. This procedure helps to preserve healthy bone
and cartilage, leading to a faster recovery compared to total knee replacement.
It is typically recommended for patients with isolated knee arthritis or joint damage that is limited to one area.
How Is Knee Replacement Surgery Done?
Knee replacement surgery is performed under general or spinal anaesthesia. The standard procedure includes:
- Incision – A surgical incision (typically 10 to 15 cm) is made at the front of the knee.
- Joint Resurfacing – Damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the femur, tibia, and patella.
- Implant Placement – Metal (titanium) and plastic components are secured to restore joint function.
- Closure – The incision is sutured, and the knee is stabilised for recovery.
How Long Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
A total knee replacement surgery typically takes 1 to 2 hours. A partial knee replacement is shorter, usually lasting 45 minutes to 1 hour. Additional time may be required for pre-surgical preparation and post-surgical monitoring.
How Long Does Knee Replacement Last?
Knee replacement implants are designed to be durable, with most lasting 15 to 25 years, depending on various factors:
- Activity Level – High-impact activities (e.g., running, jumping) can shorten implant lifespan.
- Body Weight – Excess weight increases stress on the artificial joint, leading to faster wear.
- Implant Material – Modern prosthetics use titanium and polyethylene, enhancing durability.
Studies show that approximately 82% of total knee replacements and 70% of partial knee replacements remain functional after 25 years. With proper care, many implants continue to perform well even beyond this timeframe.
Risks of Knee Replacement Surgery
As with any surgical procedure, knee replacement carries risks and potential complications that vary depending on individual health factors.
- Infection – Though uncommon, infections can be serious and may require antibiotics or, in severe cases, revision surgery.
- Blood Clots – Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can develop after surgery, necessitating blood thinners to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage – Though rare, damage to surrounding nerves or blood vessels can occur, leading to complications such as numbness, weakness, or circulation issues.
Following post-surgery care instructions can help reduce complications and promote a smoother recovery.
Cost of Knee Replacement in Singapore
The cost of knee replacement surgery varies based on the complexity, with estimated costs as follows:
| Type of Procedure | Estimated Cost (SGD) |
|---|---|
| Partial Knee Replacement | $20,000 – $35,000 |
| Total Knee Replacement | $25,000 – $40,000 |
These costs generally cover the surgery, hospital stay, and standard post-operative care,
but additional fees may apply. Pre-surgical assessments, follow-ups, and rehabilitation will
add to the overall cost.
You can claim up to $4,650 from
MediSave. Integrated Shield Plans may offer additional coverage beyond this.
Contact us
to find out more about your financial options and available coverage based on your
specific needs.
Preparing for Knee Replacement Surgery
If surgery is recommended by your specialist after conservative treatments are assessed to be no longer as effective, certain steps need to be taken before the procedure. These typically involve:
- Medical Evaluation – Blood tests and X-rays, with an MRI if needed, to assess your fitness for the procedure and identify potential risks.
- Pre-Surgery Exercises – Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstrings may be prescribed to improve stability and aid post-surgical recovery.
- Home Preparation – Arranging assistive devices (e.g., crutches, raised toilet seats) to ensure safety and help with mobility after surgery.
- Fasting Before Surgery – Reduces anaesthesia-related risks, such as aspiration and nausea.
It is essential to follow the preparatory instructions provided before surgery to ensure a smoother procedure and reduced risk of complications.
Knee replacement is a significant decision. We will explore all options first, and when surgery is the right choice, the focus is on restoring your mobility and quality of life.
Where Can I Find a Knee Replacement Specialist Near Me?
Apex Novena
admin@apexsportsclinic.sg
101 Irrawaddy Rd, #18-12 Royal Square Medical Centre, Singapore 329565
Nearest MRT: NS20 Novena (3-min walk)
Wheelchair Accessible
Apex East Coast
admin@apexsportsclinic.sg
112 East Coast Rd, #03-03/04 i12 Katong, Singapore 428802
Nearest MRT: TE26 Marine Parade (7-min walk)
Wheelchair Accessible
Why Do Patients Choose Apex Sports Clinic?
Sports Doctor in Singapore: Personalised & Affordable Care
Progressive Treatment Philosophy
We prioritise personalised, non-invasive solutions, progressing to specialised treatments, including surgery, only when needed for more effective and targeted care.
Keyhole Surgery Expertise
We specialise in advanced arthroscopic keyhole surgery to treat sports injuries with precision and minimal tissue disruption, supporting faster recovery and restored joint function.
Specialist in Sports Orthopaedics & Injury Management
We combine expert injury management with a proactive approach to maintaining your body's strength and function, so you can recover fully and perform at your peak.
Patient Journey
1 . Schedule Your Appointment

2 . Expert Diagnosis & Consultation

3 . Customised Treatment Plan

Schedule an Appointment

Our Insurance Partners








Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Knee replacement procedures in Singapore include total knee replacement (TKR), partial knee replacement (PKR), bilateral knee replacement, and revision knee replacement. The choice of procedure depends on the severity of joint damage, mobility requirements, and overall health condition.
A total knee replacement (TKR) involves removing damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing them with metal and plastic prosthetic components. The procedure restores joint function and relieves pain, making it suitable for individuals with severe arthritis or extensive joint damage.
A bilateral knee replacement refers to the replacement of both knee joints, either simultaneously or in separate procedures. A medial knee replacement is a type of partial knee replacement where only the inner compartment of the knee is replaced, typically for individuals with arthritis affecting only that area.
A partial knee replacement costs $20,000 to $35,000, while a total knee replacement ranges from $25,000 to $40,000. Costs vary based on hospitalisation, surgeon's fees, and post-surgical care. MediSave covers up to $4,650, with additional coverage available through Integrated Shield Plans and private insurance.
Knee replacement surgery is widely regarded as an effective treatment for severe knee pain and mobility issues. Most individuals experience significant pain relief and improved movement after the procedure. Studies indicate that 82% of total knee replacements and 70% of partial knee replacements remain functional after 25 years.
There is no strict age limit for knee replacement surgery. While most patients are between 60 and 80 years old, individuals over 80 can still undergo the procedure if they are medically fit. The decision is based on overall health, mobility issues, and quality of life considerations rather than age alone.
Strengthening the muscles around the knee before surgery can improve post-operative recovery. Common pre-surgical exercises include quadriceps sets, straight leg raises, heel slides, and seated knee extensions. These exercises enhance knee stability, flexibility, and overall muscle strength. It is best to consult your specialist or surgeon for personalised guidance on suitable exercises based on your condition.
Immediately after surgery, stiffness and limited mobility may make getting in and out of the bath difficult. Assistive devices such as grab bars, bath chairs, or handheld showerheads can help improve safety and ease. As mobility improves through rehabilitation, most individuals regain independence in bathing.
Knee replacement surgery is widely considered an effective solution for addressing chronic knee pain and mobility issues. Many individuals report significant improvement in movement and daily activities after the procedure. However, outcomes can vary, so it is best to consult a specialist for personalised advice.
Plastic knee replacements refer to the polyethylene components used in knee implants. These plastic inserts act as a cushioning layer between the metal components, mimicking natural cartilage and facilitating smoother joint movement.
Knee replacement may be necessary if you experience severe pain, swelling, stiffness, or limited mobility that affects daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs. If non-surgical treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, or joint injections no longer provide relief, your specialist may recommend surgery.
During knee replacement surgery, damaged cartilage and bone surfaces from the thigh bone (femur), shin bone (tibia), and sometimes the kneecap (patella) are removed. These are then replaced with metal and plastic implants to restore joint movement.
A partial knee replacement typically lasts between 15 and 25 years, with studies showing that 70% of implants still function after 25 years. The longevity of the implant depends on factors such as activity level, body weight, and the extent of joint preservation.
Knee replacement surgery is widely regarded as a beneficial and effective treatment for severe arthritis and joint damage. It can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain, enhancing overall quality of life. However, as with any surgery, risks such as infection, blood clots, and implant wear over time exist. It is best to consult your specialist to determine if knee replacement is the right option for you.
Knee replacements are typically made of titanium, cobalt-chrome, and polyethylene (plastic liners). These materials provide durability, stability, and smooth joint movement.
Knee replacement involves removing damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial implants, whereas knee reconstruction focuses on repairing ligaments, cartilage, or bones without replacing the joint. Reconstruction is often performed for sports injuries, while replacement is for severe arthritis or joint deterioration.
A total knee replacement surgery typically lasts one to two hours, while partial knee replacement is shorter, at around 45 minutes to one hour. Additional time is required for anaesthesia administration, preparation, and post-surgical monitoring.
Knee replacement surgery significantly reduces chronic pain, restores joint function, and allows patients to return to daily activities and low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling.
Yes, a hip and knee replacement on the same leg can be performed either in separate surgeries (staged approach) or simultaneously in certain cases. The best approach depends on factors such as overall health, mobility limitations, and the severity of joint damage. Consulting a specialist or surgeon is recommended to determine the most suitable option for your condition.
Titanium knee implants are designed for long-term durability, typically lasting 15 to 25 years. The longevity of the implant depends on activity levels, weight, implant material, and overall joint health. With proper care, many implants function well beyond this timeframe.
A knee replacement implant generally weighs between 400 to 800 grams, depending on the material composition, prosthetic design, and whether it is a partial or total knee replacement.
A total knee replacement usually takes one to two hours, while a partial knee replacement takes around 45 minutes to one hour. Additional time is needed for anaesthesia, pre-surgical preparation, and post-surgical monitoring.
Non-surgical alternatives to knee replacement include physiotherapy, weight management, joint injections (such as hyaluronic acid or corticosteroids), and pain-relief medications. Emerging treatments, such as stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, may also provide temporary relief for some individuals with early to moderate arthritis. However, when knee damage is severe, surgery is often the most effective long-term solution.
The advantages of knee replacement surgery include pain relief, improved mobility, enhanced quality of life, and long-term durability of the implant. The disadvantages include surgical risks, recovery time, potential complications such as infection or blood clots, and the possibility of revision surgery if the implant wears out over time.
The cost of knee replacement surgery in Singapore typically ranges between $20,000 and $40,000, depending on factors such as hospital choice, surgeon fees, and the complexity of the procedure. With insurance or MediSave, individuals may receive partial or full coverage for the surgery. MediSave allows claims of up to $4,650, while Integrated Shield Plans can provide additional coverage, depending on the policy.
Pain is expected after surgery, but modern anaesthesia and pain management techniques significantly reduce discomfort. While some soreness and stiffness may persist for the first few weeks, most individuals experience gradual relief as they recover. Pain is managed through medication, physiotherapy, and proper post-operative care.
The average cost of knee replacement surgery in Singapore ranges from $20,000 to $40,000, depending on factors such as hospital choice (public or private), surgeon's fees and post-surgery care. MediSave and Integrated Shield Plans may help offset costs, so it is advisable to check with your provider for coverage details.
Studies show that 82% of total knee replacements and 70% of partial knee replacements remain functional after 25 years. With proper care, many implants last even longer.
Yes, knee replacement is considered a major orthopaedic surgery, as it involves removing damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial implants. However, advancements in surgical techniques have led to minimally invasive approaches, reduced recovery time, and lower risks of complications.
A private hospital knee replacement in Singapore typically costs between $30,000 and $40,000, depending on the hospital, surgeon's fees, and post-surgical rehabilitation requirements. Private hospitals often provide shorter wait times and more personalised care compared to public healthcare institutions.
Most knee replacement patients are between 60 and 80 years old, as osteoarthritis and joint degeneration are more common in this age group. However, younger individuals with severe knee damage may also require surgery if non-surgical treatments are ineffective. The decision depends on overall health, pain levels, and mobility needs. It is best to consult a specialist if you experience persistent or severe knee pain and instability.
Potential downsides of knee replacement include surgical risks such as infection, blood clots, and implant loosening over time. Some individuals may experience temporary stiffness, swelling, or nerve-related issues during recovery. While most patients recover successfully, some may require revision surgery in the long term if the implant wears out.
Knee replacement surgery is a well-established procedure, but it carries risks such as infection, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), nerve or blood vessel damage, and implant complications. Individuals with pre-existing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or obesity may have a higher risk of complications. Your specialist or surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure to ensure you are well-informed.
Emerging alternatives to knee replacement include stem cell therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, and regenerative cartilage treatments. These treatments may help delay surgery for individuals with mild to moderate arthritis. However, they are not yet proven to be a permanent solution for advanced knee damage requiring replacement.
Delaying knee replacement surgery can lead to worsening pain, reduced mobility, and further joint damage. Over time, compensatory issues such as hip or back pain, muscle weakness, and joint deformities may develop. In some cases, delaying surgery can make the procedure more complex and extend recovery time.

